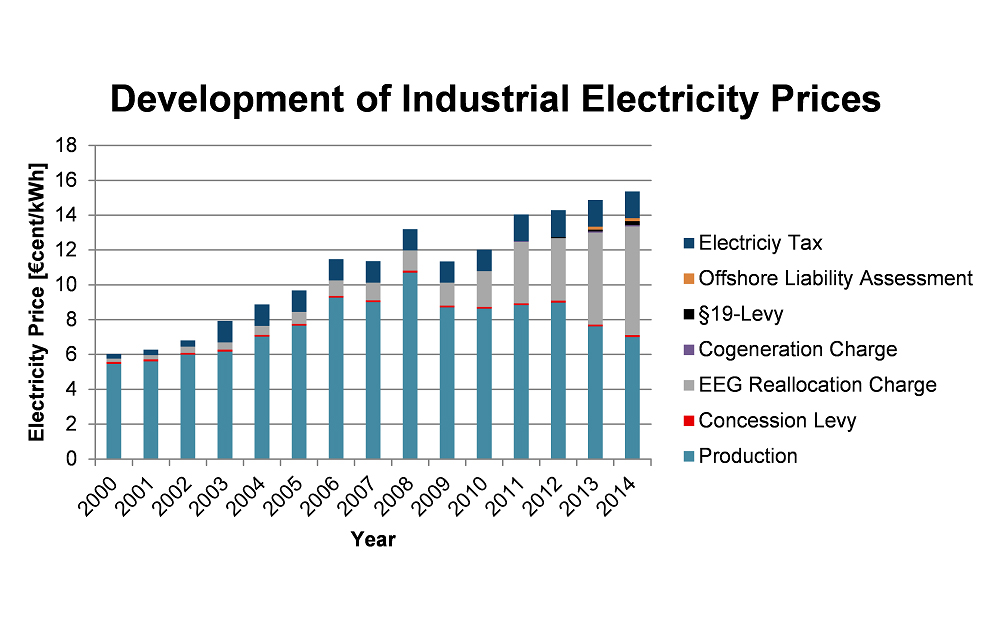
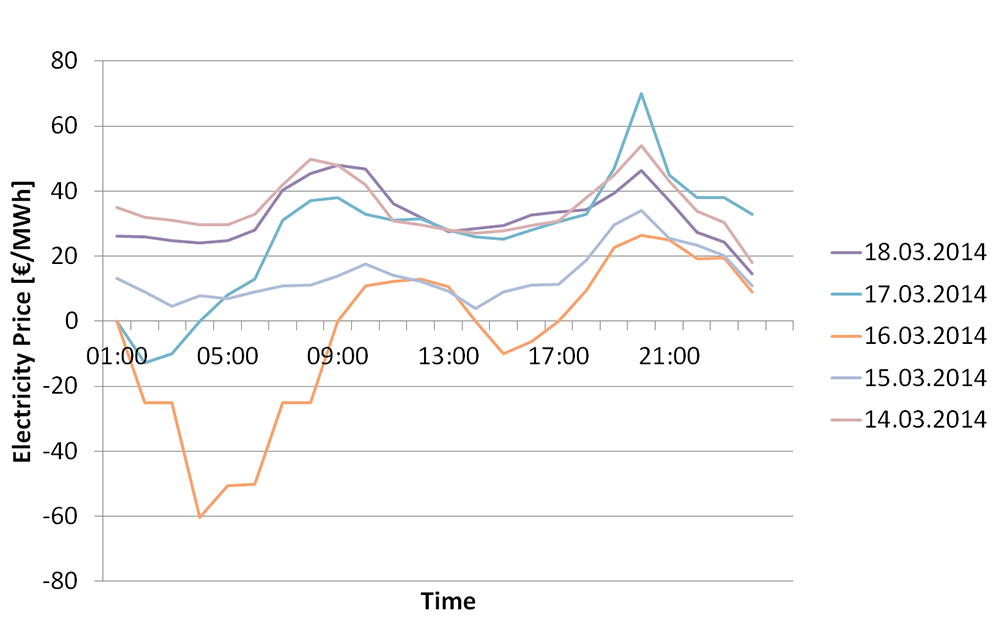
The more wind and solar energy is fed into the grid, the wider the energy price fluctuations. Industrial companies can benefit from this fact by carrying out highly energy-consuming tasks during low-price periods. In this way, electricity costs can be reduced without the need for costly investments.
For this purpose, researchers at the Institut für Integrierte Produktion Hannover (IPH) have developed a novel sequencing method for the scheduling of tasks. The ECO-S (Energy Cost Oriented Sequencing) method considers two factors: task priority and energy requirement.
In a simulation model, the researchers have compared the newly developed method to the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) scheduling method. The result is: With the ECO-S method, as many tasks as with the FIFO method were treated in due time – together with a reduction of energy costs of up to 13 percent.