"A technology with disruptive potential" – with this introduction, the start-up MIP Technology GmbH was presented at the award ceremony of the Lower Saxony Innovation Award 2020 in the category Vision. A technology is disruptive, when it has the potential to fundamentally revolutionize existing technologies and processes in production.
Magnetic identification
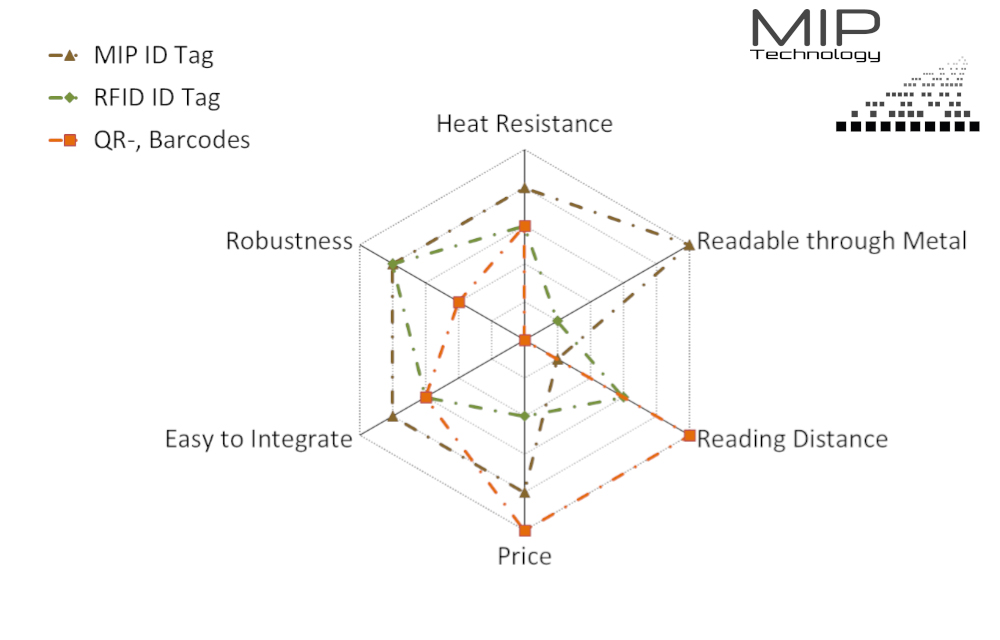
Today, optical identifiers are used to control production processes, mostly bar- or QR- codes. State of the art also includes the use of RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) transponders. Both technologies have their strengths and represent a satisfactory solution for digitizing factories in many fields of application. However, they also frequently reach their limits, for example, when used in metallic environments, at elevated temperatures, or in dirty, abrasive, and chemically active media.
As a robust alternative, MIP Technology GmbH has developed a magnetic ID for industrial environments. MIP stands for Magnetic Information Platform. The basic features of the employed technology are familiar to many people –, from the magnetic stripe on credit cards, airline tickets or local transport tickets.
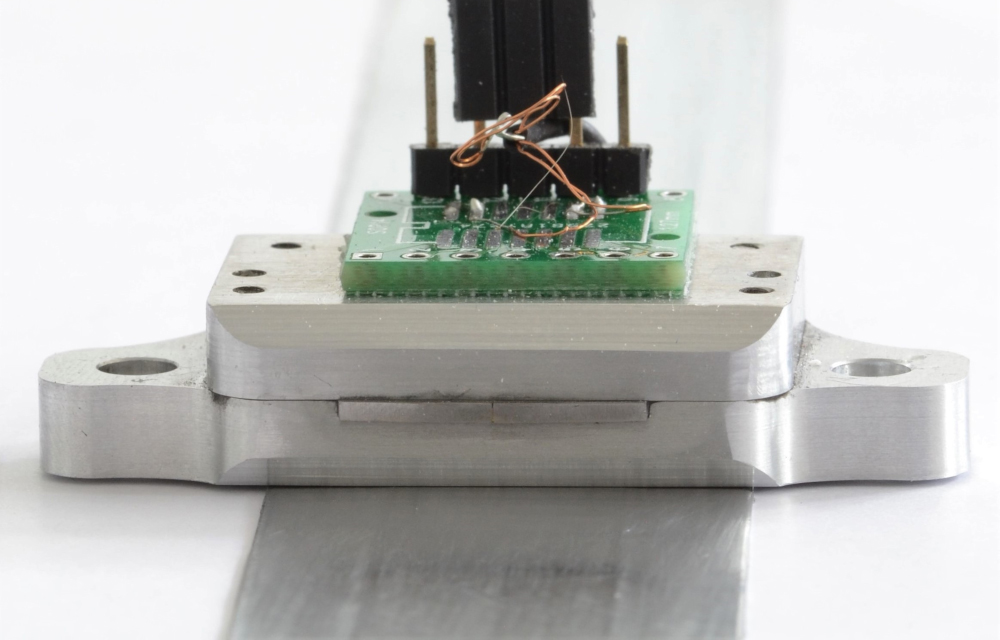
The main advantages of the Magnetic ID (MID) are its robustness, its readability through metallic layers and the fact that it contains no electronic components (see Fig. 2). In addition, the ID tags are manufactured in a roll-to-roll process, which allows magnetic IDs to be offered on the market at attractive prices.
Inexpensive, flexible and robust
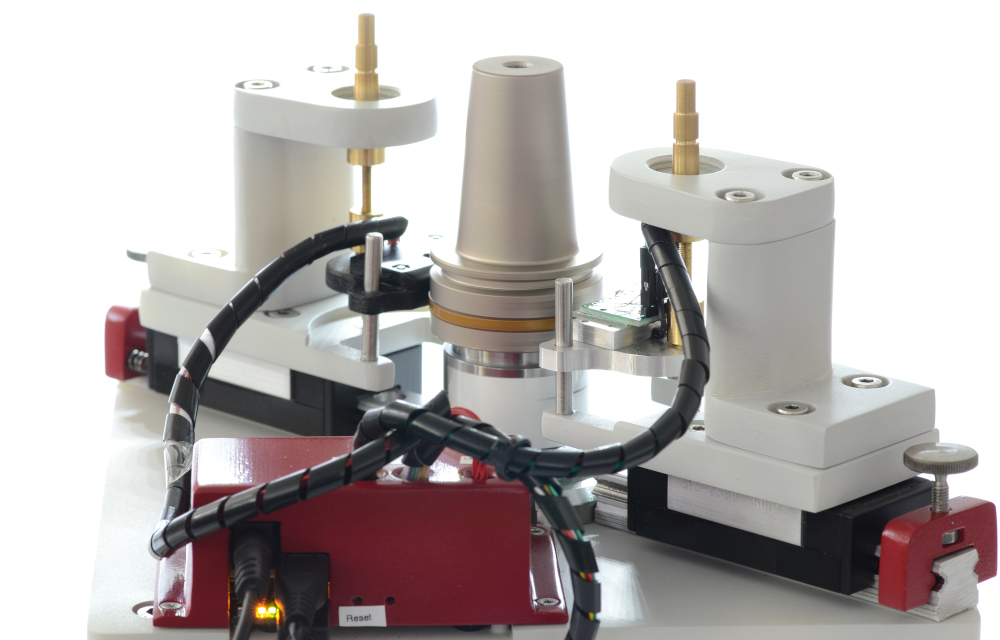
In addition to the ID tags (see Fig. 3), the magnetic information platform also includes a magnetic write head (see Fig. 4), a reading device, control electronics and a graphical user interface.
MIP Technology GmbH offers an open system: This means the software is provided free of charge and the user can integrate the read IDs into his database system. In a first stage of development, the ID Information is provided as a text file. MIP Technology GmbH aims to keep the financial hurdles as low as possible for its customers and to provide them with the maximum flexibility of their data infrastructure at the same time.
Other advantages of the magnetic ID tag are its low installation height of a minimum of 0.05 mm, its thermal stability up to 200 °C, and its insensitivity in very harsh environments.
No digitization without ID
Companies can only increase the potential of digitization through the widespread use of automated recording technologies in operating equipment and the linking of machine and process data.
For example, in the machining industry, tool life can be optimally exploited, as wear can be predicted in the future via algorithms depending on the process data. The machine controls can then compensate for wear in the production process directly. This saves money and increases throughput by reducing setup times. Similar scenarios can be developed for injection molds or other production equipment.
Identification is the key to many software solutions and numerous algorithms. The goal is to make optimal use of production equipment without risking a drop in the quality of the goods produced. In addition, the cost of replacing and overhauling production equipment will be reduced in the future, as maintenance intervals no longer follow fixed intervals, but rather can be calculated depending on the usage scenarios experienced.