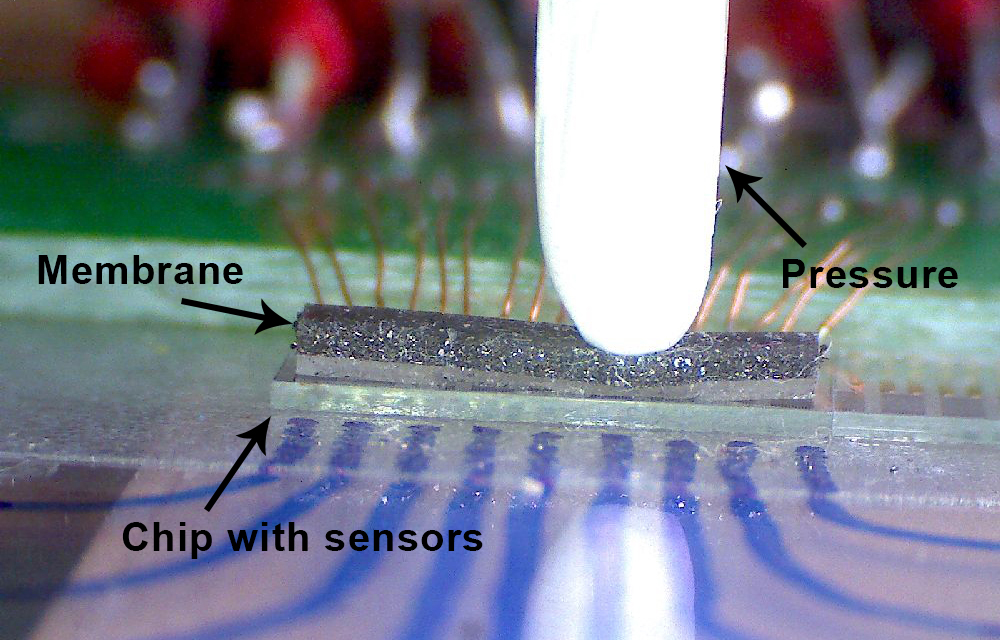
IMPT investigates a novel method, which is based on magnetism, to specifically measure contact pressure. The system consists of a membrane, which possesses magnetic properties due to embedded hard magnetic particles.
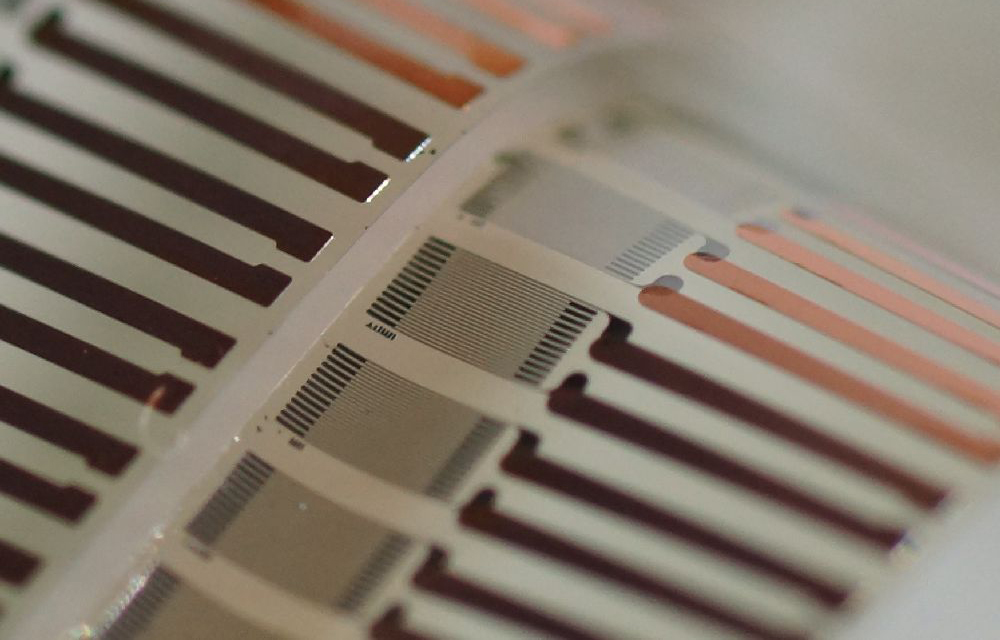
When an external force deforms the membrane, the strength of the magnetic field emitted by the membrane changes with respect to a fixed geometrical point. Placing a magnetic field sensor at the geometrical point allows an indirect measurement of the applied force (and the pressure through the area). An elastomer (polydimethylsiloxane – PDMS) is used as the membrane elastomer in combination with hard magnetic particles; the sensor is an anisotropic magnetoresistive layer.
Preliminary experiments showed a linearly proportional change in intrinsic resistance with an increase of applied force, which shows that it is in principle possible to measure pressure and determine spatial distribution, when using several sensors.