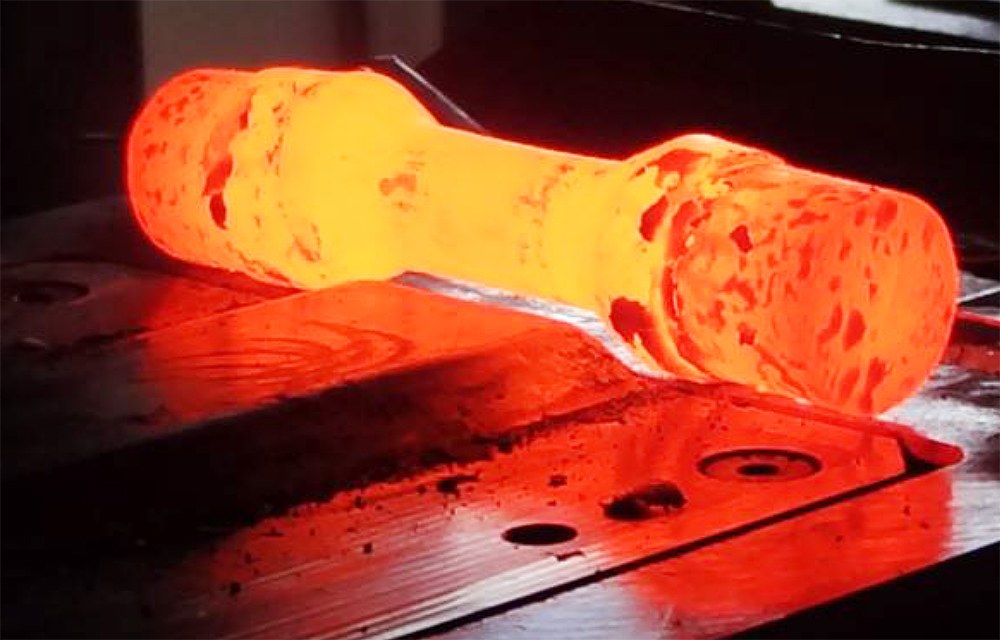
Cross wedge rolling provides for an optimum utilization of material: The cross-sectional area is partly reduced, and a pre-distribution of the material is possible without the formation of burr. However, designing cross wedge rolling processes is very complex. Depending on the material, re-adjustments are necessary with respect to forming speed, workpiece temperature and wedge angle.
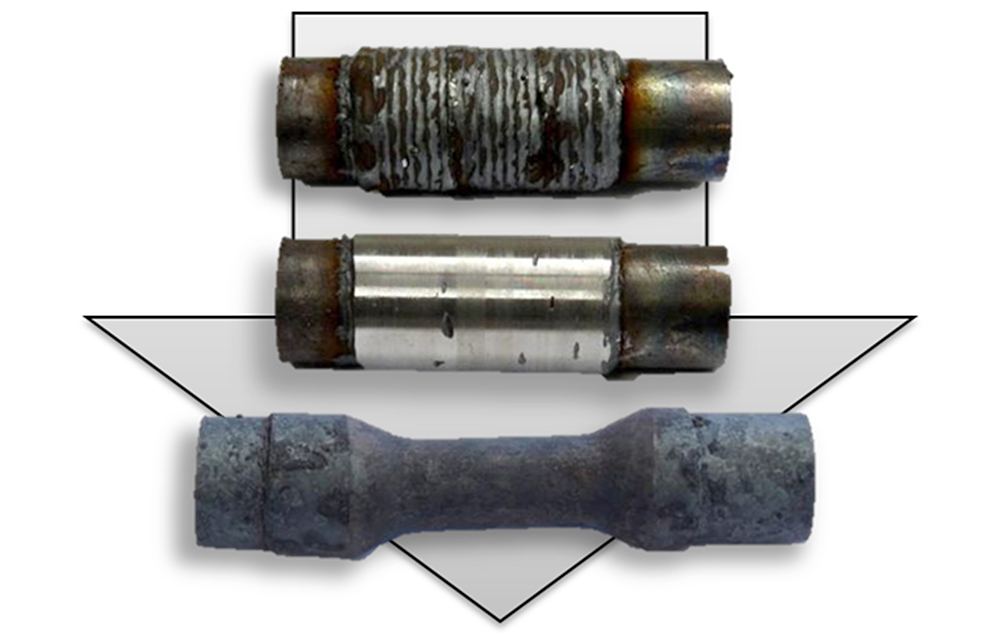
For hybrids made of steel and aluminium, the correct design of the cross wedge rolling process is even more complicated than for mono-material components, and their forming behaviour is practically unexplored so far. Within the scope of the subproject B1 of the Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) 1153, the Institut für Integrierte Produktion Hannover (IPH) is investigating on how to form hybrid billets made of different materials using cross wedge rolling. Future application examples of such components could be drive shafts in vehicles, hip implants in medical engineering or turbine blades in engines.